Discover the leading cause of blindness in adults!
Share
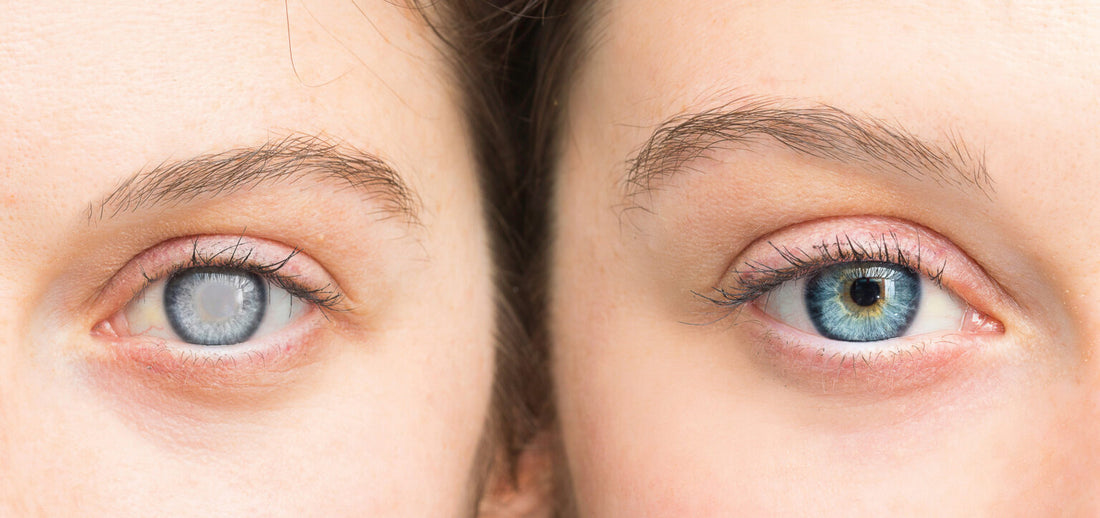
GLAUCOMA:
Glaucoma is an eye condition that occurs when the optic nerve is damaged due to higher than normal pressure . This means that the fluid inside the eye puts pressure on the inner walls, swells it like a balloon and presses on the optic nerve, which can even damage it. The problem with glaucoma is that sometimes the vision changes are so gradual that you don't notice them until the problem is already in an advanced stage.
We must keep in mind that damage to the optic nerve is irreversible , so any vision we lose cannot be recovered. Be careful with this; we shouldn't delay visits to the ophthalmologist. We must keep in mind that it is the main cause of blindness in people over 60 , so it's a good idea to check our eye pressure from time to time because it can happen at any age. If we catch it early, we can delay or even prevent vision loss. The treatment is very simple, but it will last a lifetime.
Types of Glaucoma:
There are several types of Glaucoma and to make it easier to understand, I will explain it in a very simple way:
Open Angle Glaucoma:
There is a gradual increase in pressure because the obstruction of the intraocular fluid drainage channels is partially blocked. Therefore, intraocular pressure gradually increases.
The problem is that since the damage occurs gradually, it doesn't show any symptoms and causes damage that goes unnoticed.
It is the most common glaucoma, occurring in 90% of cases.
Angle Closure Glaucoma:
This type of glaucoma is the most dangerous because the increase in intraocular fluid pressure is sudden and the drainage channels are completely blocked . It is a very rapid process that requires urgent medical attention, as vision loss can be total. This type of glaucoma presents symptoms that are quickly noticed.
Normal tension glaucoma:
This glaucoma is very rare because the optic nerve is damaged even when the patient has normal intraocular pressure. The cause is unknown.
Pigmentary Glaucoma:
In pigmentary glaucoma, the granules in the iris pigment move into the drainage canals, slowing or blocking drainage.
What symptoms can indicate that we suffer from Glaucoma?
In the open angle we will have irregular blind spots in peripheral vision and the more the disease progresses we will have tunnel vision.
In angle-closure glaucoma, there are a number of symptoms that will appear quickly:
Severe headache
Eye pain
Nausea and vomiting
Blurred vision
Redness of the eyes
If not treated urgently, it will cause long-term blindness.
Diagnosis:
When there is a suspicion of Intraocular Pressure, the doctor will perform various tests to determine the most appropriate treatment.
There are several non-invasive tests that your doctor can use:
- Measuring intraocular pressure (tonometry)
- Analyze optic nerve damage by using drops that dilate the eye.
- Check for areas of vision loss
- Measure corneal thickness
- Inspect the drainage angle
Treatment:
Once these tests are completed, one of the three available treatments will be chosen:
Eye Drops:
This is usually the first-line treatment for almost all mild cases. Fortunately, we have a wide range of medications we can use to lower intraocular pressure. These are some of the most commonly used drops:
Prostaglandins : Increase the outflow of ocular fluid: Lantanoprost, Travaprost, Tafluprost bimatoprost
Beta-blockers: Decrease the production of intraocular fluid: Timolol and Betaxolol
Alpha Adrenergic Agonists: Decrease the production of aqueous humor and increase the flow of fluid from the eye: Lopidine and Brimonidine
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Decrease the production of intraocular fluid. Dorzolamide and Brinzolamide.
Oral medication:
When drops alone are unable to lower the pressure, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the form of oral tablets are used.
Surgery:
Surgery and laser therapies are intended to improve fluid drainage within the eye.
Conclusion:
It's important to visit your optician at least once a year for a complete eye exam to prevent any possible eye damage.
